What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Since the body cannot produce them on its own, it’s important to obtain omega-3s through diet or supplements. With so many options available, choosing the best omega-3 supplement can be overwhelming. In this article, we’ll explore the health benefits of omega-3s, how to choose the best supplement, and provide a detailed guide to help you make an informed decision.
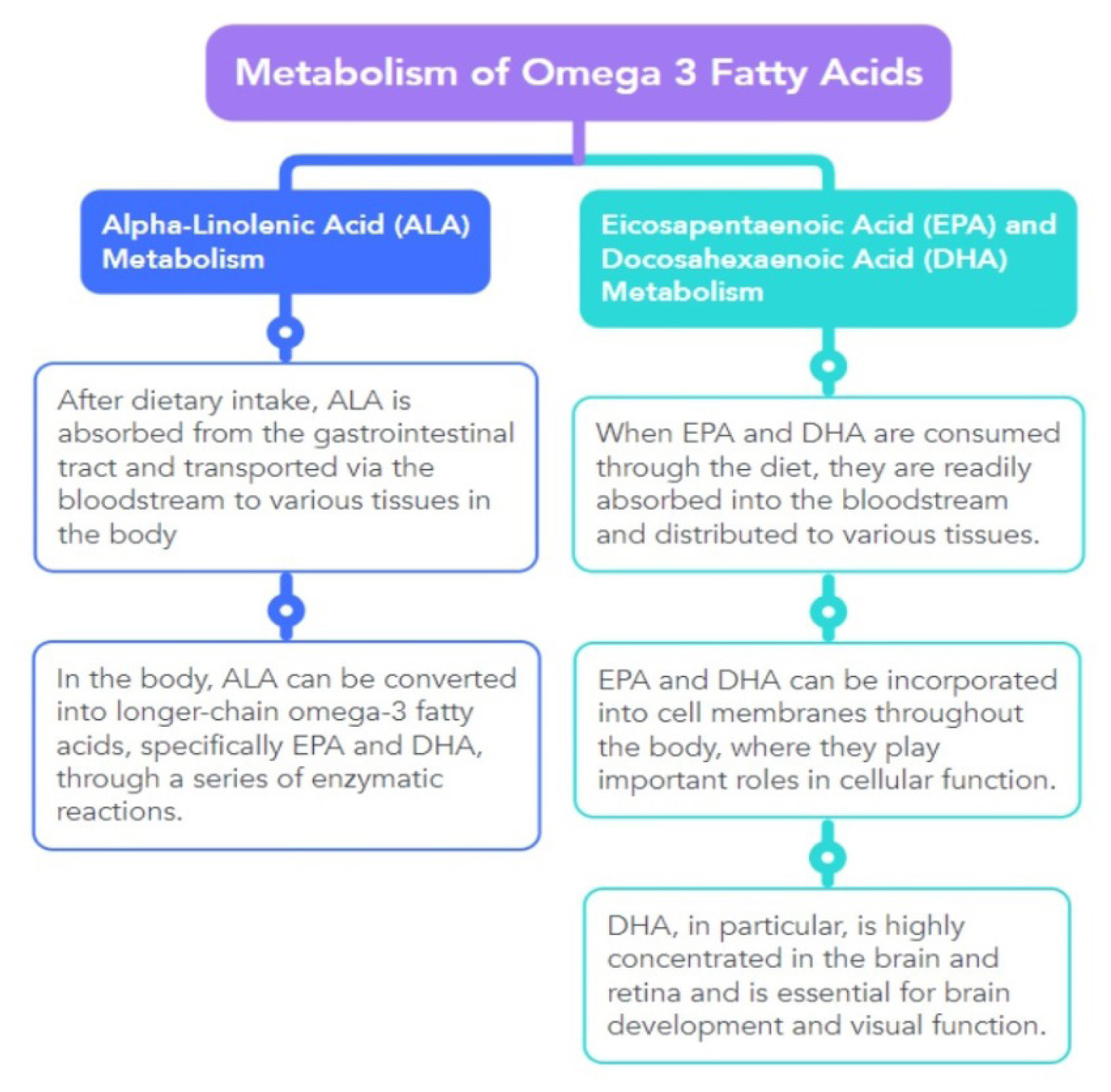
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that are essential for human health. The three main types are:
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): Found in plant oils like flaxseed and chia seeds.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Found in marine oils, supports heart and brain health.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Found in marine oils, crucial for brain and eye health.
While ALA is found in plant sources, EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish and fish oil supplements.
What are fatty acids?
Saturated fat and unsaturated fat are the two primary forms of fatty acids. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are additional breakdown products of unsaturated fat. Nutrition labels frequently use these phrases.
The chemical building blocks of fatty acids are hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon atoms arranged in a chain. The chain’s backbone is made up of carbon atoms, to which hydrogen and oxygen atoms cling to open slots.
There are no more open slots in a saturated fat. A single slot is present in a monounsaturated fat. The open slot in a polyunsaturated fat is many.
Because they raise your chance of developing certain illnesses like heart disease and stroke, saturated fats are commonly referred to as “bad” or “unhealthy” fats. When consumed in moderation, unsaturated fats—polyunsaturated and monounsaturated—support heart health, which is why they are referred to be “good” or “healthy” fats.
As a type of polyunsaturated fat, omega-3s are better for you than saturated fat.
What is the function of omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids support the proper operation of every cell in your body. They are an essential component of your cell membranes, promoting intercellular communication and giving your cells structure. All of your cells need omega-3 fatty acids, but the cells in your eyes and brain have the highest concentrations.
Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids promote the health of numerous bodily systems and give your body energy in the form of calories. These consist of your endocrine and cardiovascular systems.
Health Benefits of Omega-3s
Supports Heart Health
- Reduces triglycerides and lowers blood pressure.
- Decreases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Boosts Brain Function
- Essential for brain development in infants.
- Improves memory and cognitive function in adults.
Reduces Inflammation
- Helps manage chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis.
- Supports joint health and mobility.
Promotes Eye Health
- DHA is a major structural component of the retina.
- Reduces the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Supports Mental Health
- Reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Improves mood and emotional well-being.
Types of Omega-3 Supplements
Fish Oil
- Source: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- Benefits: High in EPA and DHA.
- Best For: General health and heart health.
Krill Oil
- Source: Tiny crustaceans called krill.
- Benefits: Contains antioxidants and is easily absorbed.
- Best For: Joint health and inflammation.
Algal Oil (Plant-Based)
- Source: Microalgae.
- Benefits: Rich in DHA, suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
- Best For: Brain and eye health
Flaxseed Oil
- Source: Flaxseeds.
- Benefits: High in ALA, which the body can convert to EPA and DHA (inefficiently).
- Best For: Vegetarians and vegans.
Cod Liver Oil
- Source: Liver of codfish.
- Benefits: Contains omega-3s along with vitamins A and D.
- Best For: Immune support and bone health.
How to Choose the Best Omega-3 Supplement
Check the EPA and DHA Content
Look for supplements with at least 500 mg of combined EPA and DHA per serving.
Look for Third-Party Testing
Choose brands that are tested by third-party organizations like IFOS, USP, or NSF for purity and potency.
Consider the Form (Liquid, Capsules, or Gummies)
- Capsules: Most common and easy to dose.
- Liquid: Great for those who dislike swallowing pills.
- Gummies: Tasty option but often contains added sugars.
Avoid Additives and Fillers
Opt for supplements free from artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives.
Check for Sustainability
Choose brands that use sustainable fishing practices or are certified by organizations like MSC (Marine Stewardship Council).
Top 5 Omega-3 Supplements
Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega
- Type: Fish Oil
- Key Features: High EPA and DHA content, third-party tested, and sustainably sourced.
- Best For: Overall health and heart health.
Thorne Research Super EPA
- Type: Fish Oil
- Key Features: High EPA content, free from additives, and third-party tested.
- Best For: Inflammation and mental health.
Garden of Life Minami Platinum Omega-3 Fish Oil
- Type: Fish Oil
- Key Features: High potency, sustainably sourced, and non-GMO.
- Best For: Heart health and brain function.
Carlson Labs The Very Finest Fish Oil
- Type: Fish Oil
- Key Features: High-quality, third-party tested, and available in liquid form.
- Best For: Joint health and inflammation.
Sports Research Triple Strength Omega-3
- Type: Fish Oil
- Key Features: High EPA and DHA content, sustainably sourced, and non-GMO.
- Best For: Athletes and active individuals.
Naturals Fish Oil
This oil is derived from the tissue of oily fish, primarily in the form of triglycerides, making it the closest alternative to consuming real fish.
Natural fish oil is rich in essential nutrients. While the composition varies by fish species, a typical 1,000 mg serving often provides around 180 mg of EPA and 120 mg of DHA. It also contains vitamins A and D.
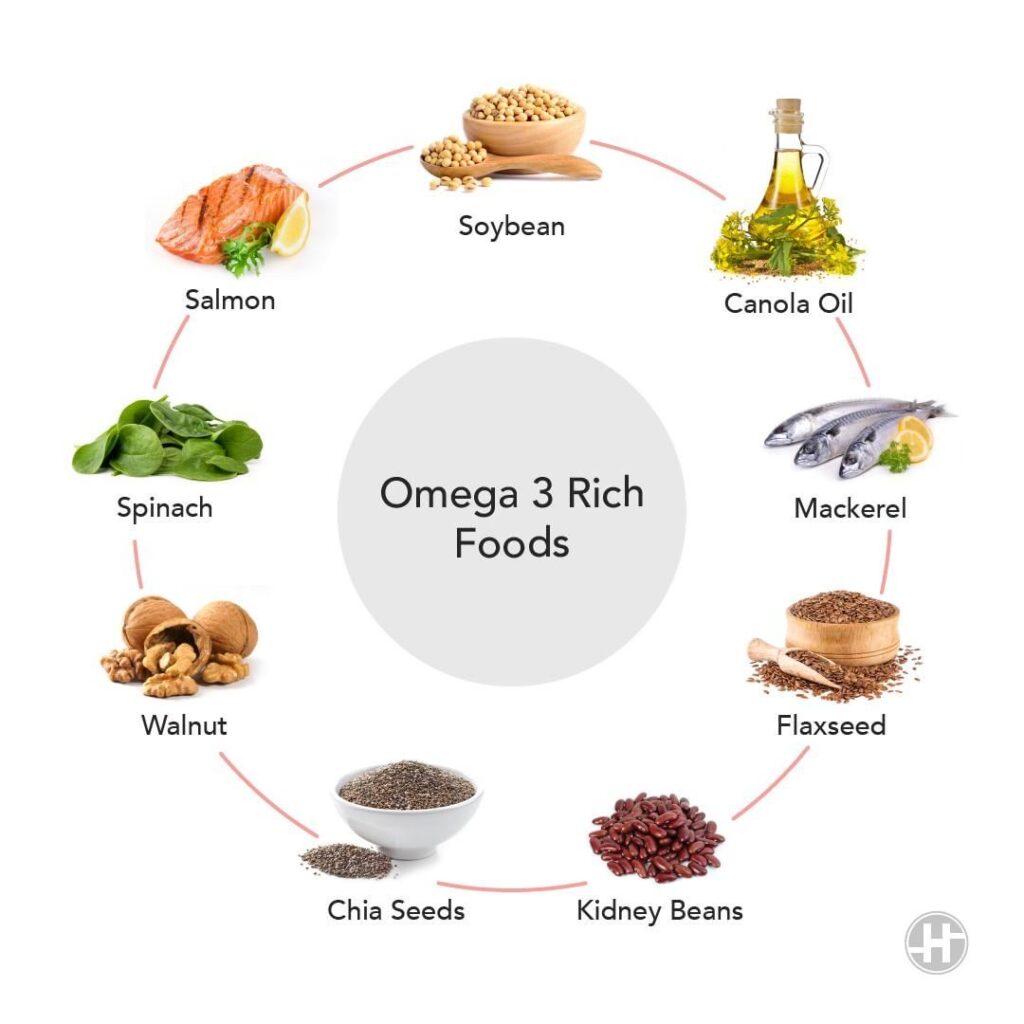
Common sources of natural fish oil include fish that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as:
when to take omega-3 supplements morning or night
Morning vs. night
Morning.
Some research indicates that consuming omega-3s with a fat-containing meal may enhance their absorption.
Night
Consuming omega-3s at night may improve sleep quality, reduce joint pain and inflammation, and help prevent fishy breath, a common side effect of fish oil supplements.
Additional factors to consider
- Consistency: Consistency is key, whether you prefer morning or night.
- Splitting doses: Splitting your supplement into two smaller doses in the morning and at night can reduce acid reflux.
- Taking with food: Taking omega-3s with food may help with absorption.
Pregnant woman and individuals with diabetes.
Pregnant women and diabetics should consult with their doctor before consuming fish oil supplements.
Side effects.
Side effects of fish oil supplements include:
- Unpleasant taste, bad breath, or bad-smelling sweat
- Headache
- Stomach problems, such as nausea, diarrhea, and heartburn
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining heart health, brain function, and overall well-being. Choosing the best omega-3 supplement depends on your specific needs, preferences, and lifestyle. Whether you opt for fish oil, krill oil, or a plant-based alternative, ensure the supplement is high-quality, third-party tested, and sustainably sourced. By incorporating omega-3s into your daily routine, you can enjoy their numerous health benefits and support your body’s optimal functioning.
FAQs
How much omega-3 should I take daily?
The recommended daily intake is 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA for adults. Consult your doctor for personalized advice.
Can I get enough omega-3s from food alone?
Yes, if you eat fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, or sardines 2-3 times per week. Otherwise, supplements can help.
Are omega-3 supplements safe?
Generally safe, but consult your doctor if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medications.
What’s the difference between fish oil and krill oil?
Fish oil is higher in EPA and DHA, while krill oil contains antioxidants and is more easily absorbed.
Can vegetarians take omega-3 supplements?
Yes, algal oil is a great plant-based source of DHA.
Disclaimer
The Content provided here is for informational purpose only. This Blog is not intended to substitute for medical advice , diagnosis , or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for any questions or concerns you may have regarding a medical condition. Writerspirit does not endorse or recommend any specific tests, physician , procedures ,opinion , or other information mentioned on the blog.