Introduction
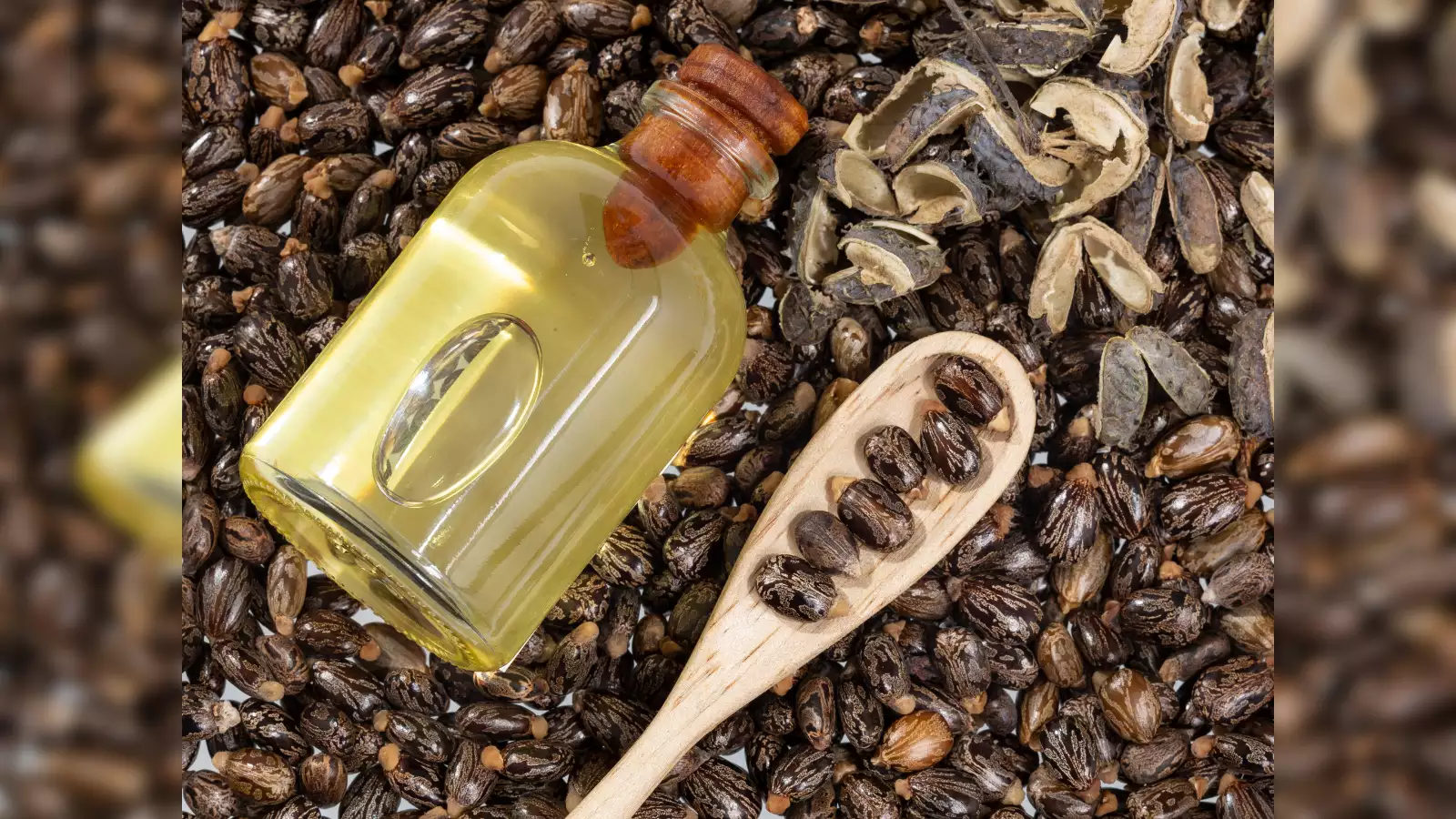
Castor oil, derived from the seeds of the Ricinus communis plant, has been used for centuries due to its powerful medicinal, cosmetic, and industrial properties. This natural oil is rich in ricinoleic acid, which gives it unique anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and moisturizing benefits. From ancient Egyptian beauty rituals to modern-day pharmaceuticals, castor oil continues to be a staple in various industries. In this article, we will explore its health benefits, average composition, and a case study showcasing its effectiveness.
Castor oil—it’s one of those remedies your grandmother might have sworn by, a bottle tucked away in the bathroom cabinet next to the Band-Aids and aspirin. But this isn’t just a nostalgic relic of old-school medicine. Castor oil has been celebrated for thousands of years across cultures, from ancient Egypt to modern-day wellness blogs. Today, it’s making a comeback, popping up in skincare routines, hair growth hacks, and even TikTok trends. But what’s the real story behind this thick, golden oil? Is it a miracle cure or just another overhyped trend?
In this deep dive, we’ll explore castor oil’s fascinating history, unpack its impressive health benefits, break down its chemical composition, and even look at a real-world case study to see how it holds up in practice. Whether you’re a skeptic or a natural remedy enthusiast, stick around—this journey into the world of castor oil might just surprise you.
The Roots of Castor Oil: A Historical Snapshot
Imagine 4000 BCE in ancient Egypt. Healers were pressing castor beans to get a multipurpose oil that could be used as a skin balm, lamp fuel, and even as a treatment for eye irritation while pharaohs were constructing pyramids. One of the earliest medical documents, the Ebers Papyrus, describes castor oil as a remedy for calming illnesses. It became known as a “multi-purpose elixir” in ancient Greece and Rome, while Ayurvedic practitioners in India called it “the secret of beauty.”
The story of castor oil didn’t end there. When supplies ran low during World War I, it was used to lubricate engines, and by the 19th century, midwives were using it to induce labour. Thanks to Gujarat’s perfect subtropical environment, the state now produces more than 90% of the world’s castor oil. From tomb remnants to contemporary medicine cabinets, this common plant has seen it all, and its resilience suggests something unique.
Why Does Castor Oil Feel This Way? An explanation of average composition
Castor oil isn’t just any vegetable oil, though. It differs from coconut or olive oil due to its special composition, which gives it lubricating and laxative qualities. Based on information from scientific analyses, the typical content of this substance is broken down as follows:
- Ricinoleic Acid (85-95%): The star of the show. This monounsaturated fatty acid is rare in nature and gives castor oil its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and muscle-stimulating effects. It’s why your intestines kick into gear after a dose.
- Oleic Acid (2-6%): An omega-9 fatty acid also found in olive oil, it adds moisturizing power.
- Linoleic Acid (1-5%): An omega-6 fatty acid that supports skin barrier function and hair health.
- Stearic and Palmitic Acids (1-2%): Saturated fats that contribute to the oil’s thick texture.
- Vitamin E (Trace): A natural antioxidant that boosts shelf life and skin benefits.
About 120 calories, zero carbohydrates or protein, and 14g of fat (mainly from ricinoleic acid) are found in one tablespoon (15g) of castor oil. It isn’t edible in the culinary sense—trust me, it tastes terrible—but it is unique in industry and medicine due to its density (0.961 g/cm³) and boiling point (313°C).
The production process is where the magic happens: boiling castor seeds deactivates the dangerous protein ricin, which makes the oil safe for usage. The adaptability of castor oil is based on this composition, which is more than merely chemistry. Let’s examine the potential health benefits.
Castor Oil’s Health Benefits: From Head to Toe
Because of its deep moisturising qualities, castor oil is frequently used in skin and hair care products. Its high ricinoleic acid concentration soothes sensitive skin, encourages hair growth, and lessens acne. Castor oil is frequently used as a natural treatment for split ends, dandruff, and scalp infections. The reputation of castor oil is not just based on exaggeration. Here are what we know about the advantages of science—and where the jury is still out—even though it is still catching up to centuries of anecdotal acclaim.
An FDA-approved natural laxative
Castor oil’s claim to fame? It’s the only FDA-approved natural laxative for temporary constipation relief. Ricinoleic acid binds to receptors in your intestines, triggering muscle contractions that push things along. A spoonful (15-60 mL) can get results in 2-6 hours—perfect for a quick fix before a colonoscopy or a stubborn blockage. But don’t overdo it; doctors warn against long-term use due to cramps and bloating.
Skin Savior: Moisturizing and Healing
Castor oil is an excellent source of hydration because of its fatty acids. A common ingredient in lotions and balms, it helps dry skin and chapped lips retain moisture (the American Academy of Dermatology even calls it a lip-healer). Consider ointments like Venelex, which combine castor oil with balsam Peru to promote healing, as an example of how its antibacterial qualities are evident in wound treatment. Although there is conflicting evidence, some people swear it helps with acne; ricinoleic acid may be helpful, but clogged pores could be a problem.
Boosts Immune System and Fights Infections
With its antibacterial and antifungal properties, castor oil helps fight infections when applied topically. It has been traditionally used to heal wounds, reduce fungal infections, and even treat minor cuts and bruises.
Hair Growth: Myth or Magic?
Does TikTok’s obsession with castor oil for hair growth work? Vitamin E and omega-6 increase scalp circulation, which may promote thicker, glossier hair. There are many anecdotes of people gleefully massaging it into thinning areas or eyelashes, but research? Slim to none. The drawback is that excessive use may result in “felting,” a rare tangling nightmare that calls for a haircut. The key is moderation.
Food and preservative
Food-grade castor oil is utilised in the food sector as a mould inhibitor, flavouring, confectionery (such as chocolate’s polyglycerol polyricinoleate), and packaging. Additionally utilised in the food industry is polyoxyethylated castor oil, such as Kolliphor. Castor oil is used to preserve food grains in India, Pakistan, and Nepal. It prevents the rotting of beans, wheat, and rice. The legume pigeon pea, for instance, is frequently offered with an oil coating for prolonged storage.
Joint Pain Relief and Anti-Inflammatory Power
Do you have knee pain? Ricinoleic acid, which has been shown in animal experiments to reduce swelling when given topically, is the source of castor oil’s anti-inflammatory properties. According to a human trial, it relieved knee arthritis just as well as NSAIDs without the negative side effects. You may notice a difference if you rub it on or apply a castor oil pack, which is a hot cloth soaked in oil. Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, castor oil is commonly used in massage therapy to relieve arthritis pain and muscle soreness. Applying warm castor oil compresses on affected areas can help reduce stiffness and improve joint mobility.
Labor Induction: A Traditional Twist
Midwives have used castor oil to kickstart labor for centuries—93% of U.S. midwives in 1999 relied on it. It works by irritating the bowels, which can nudge the uterus into action, plus it boosts prostaglandin production to ripen the cervix. A 2018 study showed 91% of women who took it delivered vaginally, but nausea and diarrhea are common downsides. Pregnant? Talk to your doctor first.
Extra Advantages: Eyes, Dentures, and More
- Denture Care: Studies suggest soaking dentures in a 10% castor oil solution kills bacteria and fungi like Candida, reducing infection risk.
- Eye Health: Ayurvedic tradition uses it for dry eyes, and some OTC drops include it to cut tear evaporation—though never drip pure oil into your eyes (ouch, infections!).
- Immune Boost: Early research hints it might tweak white blood cell counts, but it’s a long shot for now.
Although castor oil has a wide range of uses, it is not a panacea. Let’s use an actual case to see how well it performs.
Case Study: Castor Oil Packs for Constipation Relief
Researchers tested castor oil packs on elderly patients suffering from persistent constipation in a 2011 trial conducted at a long-term care facility. The setup: two groups of 35 people, each with an average age of 82. For a week, one group applied castor oil packs—flannel soaked in oil—to their abdomens using heat for 60 minutes each day. Sennosides and other common laxatives were given to the other.
Results: Both groups saw relief—fewer strains, more regular bowel movements. But here’s the kicker: the castor oil group reported zero harsh side effects, while the laxative crew dealt with cramps and urgency. Why? Ricinoleic acid likely penetrated the skin, easing inflammation and nudging the intestines gently.
Takeaway: For mild constipation, castor oil packs might rival conventional options with less drama. More studies are needed, but it’s a promising nod to tradition meeting science.
Average Composition of Castor Seed Oil
Castor oil is unique due to its high ricinoleic acid content, which accounts for approximately 85-90% of its composition. Below is the average composition of castor seed oil:
| Component | Percentage (%) |
| Ricinoleic Acid | 85-90% |
| Oleic Acid | 4-6% |
| Linoleic Acid | 2-4% |
| Stearic Acid | 1-2% |
| Palmitic Acid | 1-2% |
This composition makes castor oil a highly versatile ingredient in medicinal, cosmetic, and industrial applications.
How to Use Castor Oil Safely
Ready to try it? Here’s the lowdown:
- For Constipation: 1-4 tablespoons orally, mixed with juice to mask the taste. Wait 2-6 hours.
- Skin/Hair: Massage a few drops into the target area. Patch-test first to avoid irritation.
- Packs: Soak a cloth, apply to skin, cover with plastic, and add a heating pad for 30-60 minutes.
- Dentures: Soak in a 10% solution for 20 minutes.
Start small—castor oil is potent. And if you’re pregnant or have gut issues like IBD, skip it unless a doctor green-lights it.
The Flip Side: Potential Risks and Side Effects
Not all castor oil is perfect. Chronic constipation, nausea, or diarrhoea may result from overusing it as a laxative. It may cause allergies (think rashes or itching) or clog pores on the skin. In the eyes? Use only prepared drops; non-sterile oil increases the risk of infection. And induction of labour without medical supervision? dangerous enterprise. Here, moderation and prudence are your friends.
Why Castor Oil Still Matters Today
In a world of synthetic drugs and quick fixes, castor oil’s natural roots keep it relevant. It’s affordable, versatile, and bridges ancient wisdom with modern needs—think eco-friendly lubricants or vegan skincare. Social media might overhype it, but its FDA-backed laxative status and growing research keep it grounded. It’s not about replacing medicine; it’s about complementing it.
Conclusion: Is Castor Oil Really Worth the Hype?
While castor oil isn’t a panacea, it’s also not a placebo. Its benefits, which are supported by research, history, and actual outcomes like our case study, range from relieving constipation to calming joints. It isn’t for everyone or every issue, though. Growth of hair? Can we cure cancer? Nope, don’t trust the outrageous statements. Castor oil is a natural powerhouse with a wide range of benefits, from improving skin and hair health to aiding digestion and reducing inflammation. Its unique composition makes it a valuable ingredient in beauty, wellness, and pharmaceutical industries. With its growing popularity, castor oil remains a go-to solution for those seeking natural remedies.
So, if you’re interested, grab that bottle, but make good use of it. Castor oil: have you tried it? Please share your experience below; I’d be interested in knowing how it went—or didn’t!
Can I use castor oil every day?
It depends on the purpose. For skin or hair, a few drops daily is usually fine if you don’t experience irritation—always patch-test first! As a laxative, though, stick to occasional use (1-4 tablespoons as needed) to avoid dependency or side effects like cramps. Check with your doctor for long-term use.
Does castor oil really help with hair growth?
Anecdotally, yes—many swear by it for thicker hair or longer lashes, thanks to its omega-6 and vitamin E content. But scientific studies are limited, so results vary. Use sparingly to avoid buildup, and don’t expect overnight miracles.
Is castor oil safe for pregnant women?
Not without medical advice. While it’s traditionally used to induce labor, it can cause nausea, diarrhea, or complications if misused. If you’re pregnant, consult your doctor before trying castor oil for any purpose.
How do I apply a castor oil pack?
Soak a flannel cloth in castor oil, place it on the target area (like your abdomen for constipation), cover with plastic wrap, and apply a heating pad for 30-60 minutes. Relax, then wash off the oil. It’s a soothing ritual!
Can castor oil treat acne?
It’s a mixed bag. Its antimicrobial properties might help, but its thick texture can clog pores for some, worsening acne. If you’re acne-prone, try a small test area first or opt for lighter oils like tea tree.
What’s the difference between regular and Jamaican black castor oil?
Jamaican black castor oil is roasted before pressing, giving it a darker color and nuttier scent. Some say it’s better for hair growth due to higher ash content, but both types share similar core benefits. Pick based on your preference!
Are there any side effects I should watch for?
Yes—overusing it as a laxative can lead to diarrhea or nausea. On skin, it might cause rashes if you’re allergic. Never use pure oil in your eyes (stick to formulated drops), and avoid it if you have conditions like IBD without a doctor’s okay.
Castor oil boling and freezing point
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Boiling Point: 313°C (595°F)
Freezing Point: -10°C (14°F)