Improve results with prompt engineering strategies.
This manual offers methods and techniques for improving the performance of big language models, sometimes known as GPT models, such as GPT-4o. For maximum impact, the techniques outlined here can occasionally be used in conjunction. We encourage you to try out several approaches to see which ones work best for you. The quality of the outcomes that artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) generate now greatly depends on how you ask it. Prompt engineering is useful in this situation. The art and science of creating and improving input prompts to direct AI models (such as GPT-4, for instance) to produce the most precise, pertinent, and practical results is known as prompt engineering.Whether you’re a writer, developer, digital marketer, or AI enthusiast, learning prompt engineering can significantly increase your output and innovation. In addition to offering you 200 sample prompts from a variety of genres, this blog will go into great detail about prompt engineering, its significance, and how to become an expert at it.
The Value of Prompt Engineering
Innovative Solutions, a digital business, sought to create a tool for its marketing team that would generate content using artificial intelligence. The business used GPT-3 to assist in creating newsletters, blog entries, and social media content. The outcomes were poor at first. The content either lacked the proper tone for the brand or was overly generic.
The team began to observe improved outcomes after devoting time and money to quick engineering and prompt refinement. They customised their prompts to be more precise, informing the AI about their target audience, the tone of voice, and the kind of content they wished to produce, rather than merely asking it to “write a blog post.”Think about a marketing team that wants to provide interesting material for social media. At first, they enter ambiguous instructions such as “Write a post about our product.” The stuff produced by the AI was uninspired and boring.
Their requests became more structured as prompt engineering techniques were used: “Create a 150-character Facebook post supporting our environmentally friendly water bottles, emphasizing their advantages and fostering audience engagement.” The outcome was an engaging piece that connected with their target audience, proving that thoughtfully written prompts may produce excellent outcomes.
For Example: Before prompt engineering: “Write a blog post about artificial intelligence.” After prompt engineering: “Write a 500-word blog post on the impact of artificial intelligence on digital marketing in 2024, using a professional and engaging tone for marketing professionals.”
The results were clear. The more specific and well-crafted the prompts were, the better the content became. In this case, prompt engineering helped bridge the gap between AI’s potential and the company’s specific needs.
The Science Behind Prompt Engineering
How AI Models Understand Prompts
Based on the input they receive, AI models like as GPT-4 predict the most likely next word or phrase. These models can process text based on patterns, context, and likelihood since they have been trained on enormous volumes of data. However, the quality and specificity of the input prompt have a significant impact on their answers.
Types of Prompts: Structured vs. Unstructured
Prompts can be classified as structured or unstructured. Structured prompts are those that are highly specific and well-defined, often containing clear instructions, guidelines, or rules. Unstructured prompts, on the other hand, are more open-ended, which might lead to more creative or varied outputs.
Understanding Context in Prompts
Problem:
In the fast-evolving landscape of AI, the ability to communicate effectively with models is crucial. Many users struggle to get the desired output from AI because they lack the know-how to craft effective prompts. This challenge can lead to frustration and wasted time, preventing individuals and organizations from fully leveraging AI’s capabilities.
Agitate
Imagine spending hours on a project, only to receive generic and unhelpful responses from an AI model. This is a common scenario faced by users who are unaware of how to structure their prompts. The stakes are high—businesses risk falling behind their competitors who harness the power of AI effectively. Moreover, in fields like content creation, marketing, and data analysis, poorly designed prompts can result in subpar outputs that do not meet the needs of the target audience.
Best Practices for Writing Effective Prompts
Crafting Clear and Concise Prompts
The more specific and detailed the prompt, the better the model will understand the desired outcome. Avoid vague instructions and focus on clarity.
Iterative Testing and Refinement
Experimenting with different versions of a prompt is essential. Try refining the prompt based on the AI’s outputs to identify what works best.
Controlling Tone, Style, and Output Length
Prompt engineers can guide the tone, style, and length of responses by including specific instructions. For example, if a formal tone is required, this can be clearly indicated in the prompt.
Dealing with Ambiguity and Bias in Prompts
Ambiguous prompts can confuse AI models, leading to incorrect or biased responses. It is crucial to ensure that prompts are specific and neutral, minimizing any unintended bias in the AI’s answers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Prompt Engineering
Overcomplicating Prompts
While specificity is important, overly complex prompts can confuse AI models. Simplicity and clarity are often the keys to success.
Lack of Specificity
A vague prompt like “Write a story” will lead to unpredictable results. Being clear about the genre, tone, and setting can help the AI produce a more relevant output.
Ignoring Model Limitations
It’s essential to understand the limitations of the AI model you’re working with. Overestimating its capabilities can lead to unrealistic expectations.
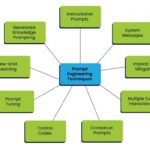
Advanced Techniques in Prompt Engineering
Prompt Chaining
Prompt chaining involves using the output from one prompt as the input for another. This technique allows for more complex tasks and detailed responses.
Using Conditional Statements
Conditional prompts can guide the AI to produce responses based on specific conditions, leading to more nuanced outputs.
Utilising Memory and Contextual Information
Advanced prompt engineers can leverage contextual information and even “memory” to build prompts that evolve over time, tailoring responses based on past interactions.
Fine-tuning Prompts for Specific Applications
In certain industries, fine-tuning AI models with specialised prompts can result in more accurate and effective outputs for niche tasks.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering will only become more important as AI develops. There will be a greater demand for qualified quick engineers as AI models and tools progress.A key ability for maximizing AI’s potential is prompt engineering. You may make sure AI produces useful, accurate, and significant results by comprehending the subtleties of prompt crafting, testing, and improving.
FAQs.
Practical Examples of Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering for Content Creation
AI can assist in writing blog posts, articles, or social media content. Crafting a prompt that specifies the target audience, tone, and length can lead to more customized content.
Prompt Engineering for Code Generation
AI models can help generate code snippets based on clear, well-structured prompts. These can range from simple function requests to complex algorithms.
Prompt Engineering for Customer Support Automation
Customer support AI systems benefit from well-designed prompts that can lead to natural, helpful, and contextually appropriate responses.
Prompt Engineering for Data Analysis
Data analysts can use AI to analyze datasets and generate insights. Clear prompts can guide the model to interpret the data and offer actionable insights.
Why is prompt engineering important?
The quality of AI outputs is enhanced and ambiguity is decreased with careful prompt engineering. This is particularly crucial in areas where clarity is crucial, such as professional communication, educational materials, and customer service.
How can I make prompts more specific?
Set clear expectations, ask direct questions, and provide pertinent context. Instead of asking, “Tell me about climate change,” for example, a more targeted question may be, “Explain the primary causes of climate change and its impact on agriculture in the next 10 years.”
What techniques improve prompt quality?
Context: Providing background information helps the AI understand your requirements.
Direct questions: Ask focused, direct questions to get to the point quickly.
Layered prompts: Break down complex queries into simpler, step-by-step questions.
Specify format: If you want lists, comparisons, or step-by-step answers, make this clear in your prompt.
What are examples of effective prompt structures?
List format: “List the top five strategies for improving SEO for new blogs.”
Comparative prompts: “Compare the advantages and disadvantages of prompt engineering for different AI platforms.”
Creative prompts: “Create a detailed outline for a blog post about AI in education.
Can prompts be used for generating SEO-friendly content?
Yes, prompt engineering can help generate SEO-friendly content by asking for structured responses that use relevant keywords, headings, and concise information tailored to audience searches.
What are some common mistakes in prompt engineering
Being vague: Without clear direction, AI responses may be too broad.
Long-winded prompts: Overly complex prompts can confuse the model.
Omitting important context: Forgetting to mention specific details can lead to less relevant answers.
How does prompt engineering benefit bloggers?
Bloggers can use prompt engineering to brainstorm topics, generate outlines, and ensure SEO compliance. For example, prompts can help identify trending keywords or create optimized article headings and descriptions