How to Build Self-Control
Introduction.
One of the most crucial abilities for living a successful and balanced life is developing self-control. The ability to utilize self-control is essential for reaching your objectives, whether they involve improving your eating habits, concentrating on a challenging task, or maintaining composure under pressure. Now let’s explore the crucial actions you may do to improve your self-control.
The capacity to restrain one’s feelings, ideas, and actions—particularly in the face of temptations or impulses—is known as self-control. It is what enables you to stop, consider your options, and decide logically as opposed to impulsively. Our life can go out of hand if we lack self control. Although making snap decisions might make you feel good in the moment, they might have long-term effects that hinder your ability to advance both personally and professionally.
Benefits of Building Self-Control.
Improvements in health
You are more likely to stick to healthy routines like regular exercise, eating well-balanced meals, and getting adequate sleep when you learn self-control. These routines support both physical and emotional health.
Enhanced decision-making.
Control improves your ability to consider your options and make well-informed decisions. Your ability to weigh risks and rewards will improve, which is important for making decisions about everything from daily activities to careers.
Improved connections
Reliability to others depends on your ability to regulate your feelings and responses. You’ll be more composed, less prone to lose your cool, and more adept at handling disagreement amicably.
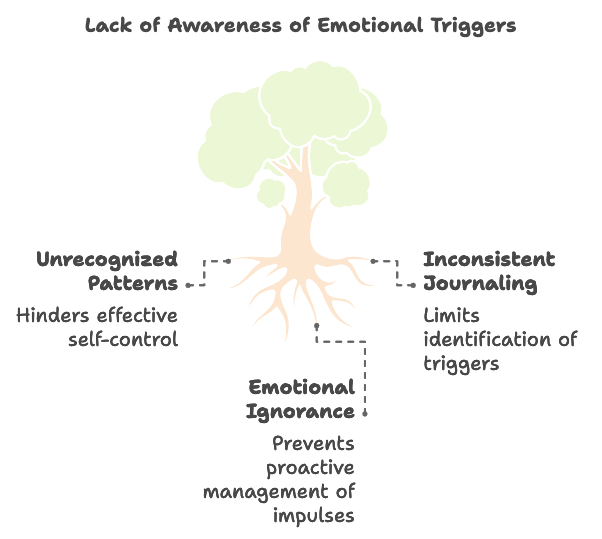
Identify Your Triggers
The power of awareness
Acquiring self-control begins with knowing what sets off your impulsive actions. These could be particular feelings, circumstances, or even individuals. Being aware of your triggers is essential because it allows you to start effectively managing them once you identify them.
How to recognise your emotional triggers
Begin by maintaining a journal. Jot down the circumstances, people you were with, and your feelings at every time you felt like you lost control. You’ll see patterns that assist you identify issues that need to be fixed.
Set Clear Goals
The importance of having a purpose
You have something to strive for when your goals are clear. Self-control can seem meaningless without a clear goal because you’re not sure what you’re aiming for.
Breaking down big goals into manageable steps
or example, if you want to lose weight, don’t focus solely on the final number you wish to reach. Break it down into smaller, achievable goals like cutting out sugary snacks or exercising three times a week. Small wins lead to big results over time.
Put mindfulness into practice.
What is mindfulness?
The ability to be totally present and involved in whatever you’re doing at any one time is known as mindfulness. It entails objectively monitoring your emotions and ideas.
How mindfulness strengthens self-control
You can prevent impulsive reactions from becoming out of control by practicing mindfulness. By remaining in the moment, you allow yourself to take a more deliberate response by causing a pause between impulse and action.
Create a Supportive Environment
Why environment matters
Your environment plays a significant role in how easily you can maintain self-control. If you’re surrounded by distractions and temptations, it’s harder to stick to your goals.
Removing temptations and distractions
Be proactive in clearing your surroundings of stressors. For instance, avoid keeping unhealthy snacks around the house if you frequently eat junk food as a late-night snack. Into the distance, out of mind!
Establish Healthful Habits
How habits develop
When a behaviour is repeatedly performed in response to a signal and results in a reward, a habit is formed. This behaviour eventually turns into an automatic one.
Repetition’s function in self-control
Good habits are formed by regular practice, which lessens the need for willpower. For instance, if you make it a practice to read for ten minutes every morning, it will eventually become second nature to you.
Make Use of Encouragement
The principles of reward science
By providing a reward, positive reinforcement motivates you to repeat desired behaviours. Reaching a milestone might be as easy as rewarding yourself with a small purchase.
Ways to treat yourself to rewards without going crazy
Maintaining proportionate rewards is crucial. You can stay motivated by rewarding yourself for little accomplishments, like finishing a task on time. Just watch out that the incentives don’t get in the way of your progress—for example, don’t treat yourself with a whole cake after a week of eating healthily).
Exercise Postponed Gratification
Delay in gratification: what is it?
The capacity to withstand the lure of an instant reward in favour of a larger or better one later on is known as delayed gratification.
Why it is essential for sustained success
Because many of life’s greatest rewards—like career success, solid relationships, and financial stability—require patience and perseverance, learning to master delayed gratification is essential. Anticipating a larger benefit frequently yields more significant and fulfilling results.
Effectively Handle Stress
The effects of stress on self-control
One of the main things that undermines self-control is stress. Stress causes your brain to go into survival mode, which makes it more difficult to think properly and stay on course with your objectives.
Techniques for managing stress
Include stress-relieving activities in your routine, such as deep breathing, meditation, or physical activity. By calming your mind, these techniques help you stay in control even in trying circumstances.
Practice Self-Compassion
Why it’s important not to be too hard on yourself
It’s natural to make mistakes while working on self-control. The key is to forgive yourself and learn from the experience, rather than giving up entirely.
How self-compassion helps in building resilience
By being kind to yourself, you foster a growth mindset, which helps you bounce back from setbacks and keep moving toward your goals.
Evaluate Your Development Frequently
The ability to reflect
Reviewing your progress on a regular basis will help you stay on course. Consider the tactics that are effective and the areas in which you still need to grow.
modifying your strategy in light of advancements
Never be scared to change course if something isn’t working. Being able to exercise self-control involves constant improvement, so be adaptable and willing to try new things.
Avoid these common mistakes when developing self-control: overcommitting
Burnout can result from attempting to adjust too many things at once. Take it slow and concentrate on one thing at a time.
Insufficient patience
Gaining self-control takes time and effort. Refrain from giving up if you don’t get results right away.
Conclusion
The Path to Self-Control Is Not a Destination.
Although developing self-control requires patience, persistence, and time, the benefits are priceless. You’ll progressively improve your capacity to maintain focus, withstand temptation, and make choices that are consistent with your long-term objectives by putting these methods into practice. Recall that progress, not perfection, is what self-control is all about.
FAQs
What is the duration required to develop self-control?
Developing self-control is a continuous process that is unique to each person. Depending on where you are beginning from and the habits you want to form, it could take weeks or months.
Can one develop better self-control at any age?
It is possible to develop self-control at any age. Throughout life, the brain can continue to create new patterns and behaviours.
What distinguishes self-control from willpower?
While self-control is a more general ability to reliably govern behaviour across time, willpower is the momentary strength to resist temptation.
How does self-control relate to diet?
Eating a well-balanced diet can help with self-control since it helps improve brain function and lessen mood swings, which can cause impulsive behaviour.
How do I respond if I make a mistake?
Be gentle with yourself if you make a mistake. Admit your error, draw lessons from it, and proceed. To recover, self-compassion is essential.